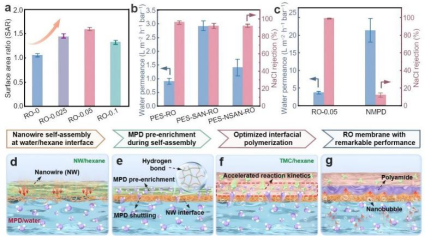
Recently, the research team led by Prof. Zhiwei Wang from CESE published their latest findings in Nature Communications. The study proposed a novel membrane fabrication strategy based on amphiphilic nanowire-mediated monomer shuttling, leading to the creation of ultra-selective reverse osmosis (RO) membranes for water treatment. These advanced RO membranes exhibited substantially enhanced removal performance for small, neutral organic contaminants (SNOCs). This work provides new insights for the precise construction of high-performance RO membrane materials and the development of novel RO water treatment technologies. It also holds promising significance for the future design and optimization of next-generation membrane materials.
Article Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-61488-5